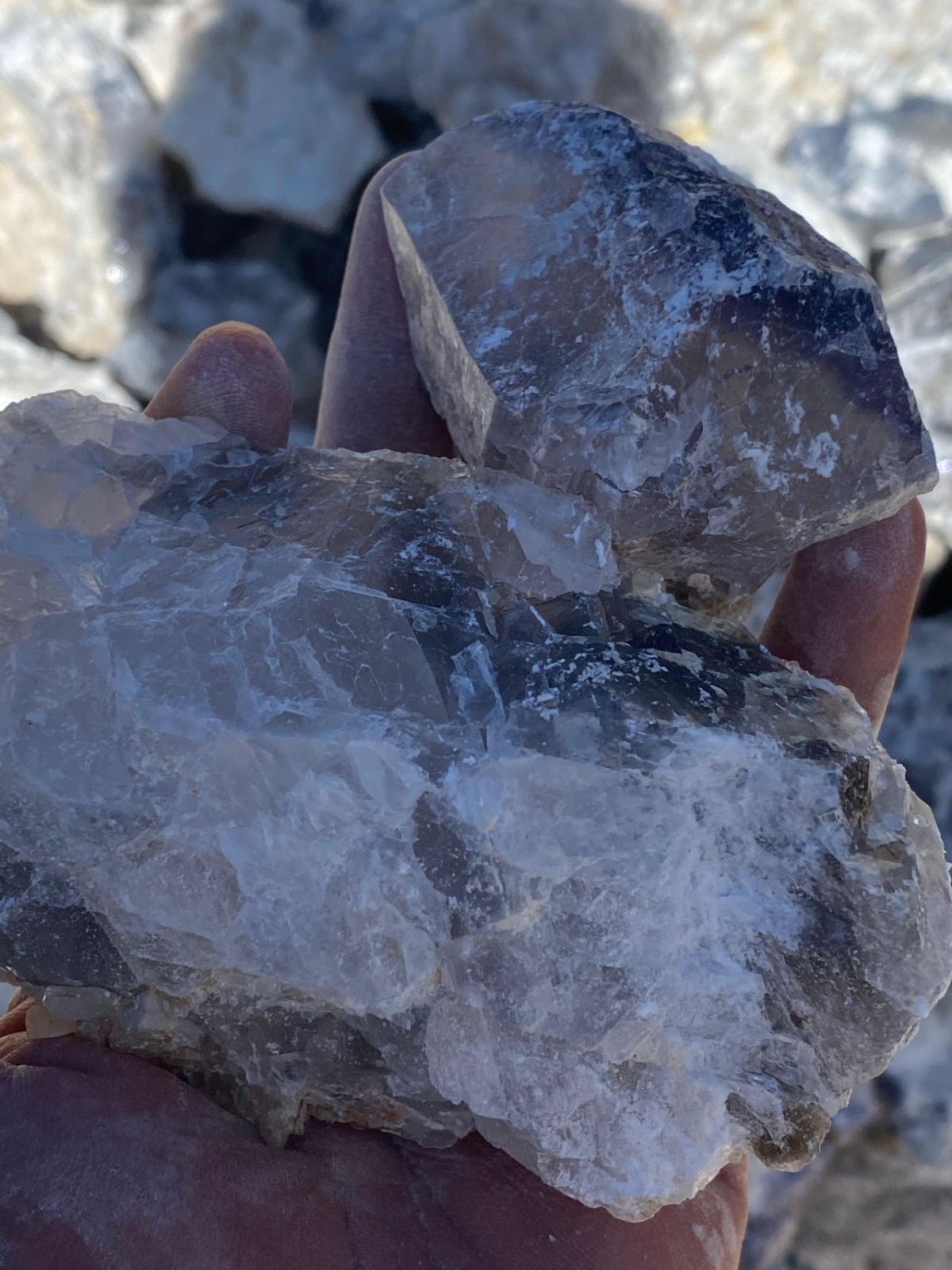
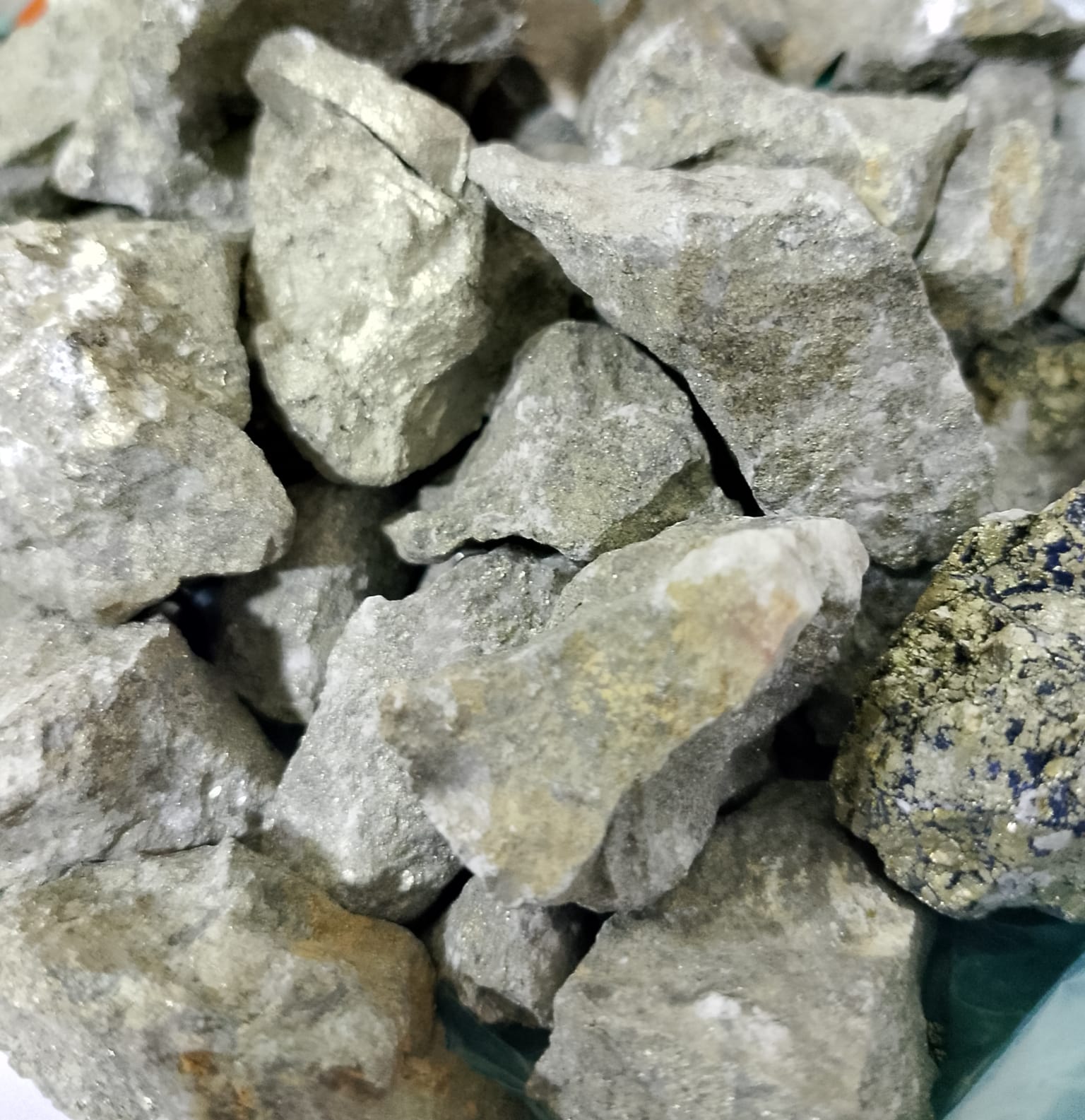
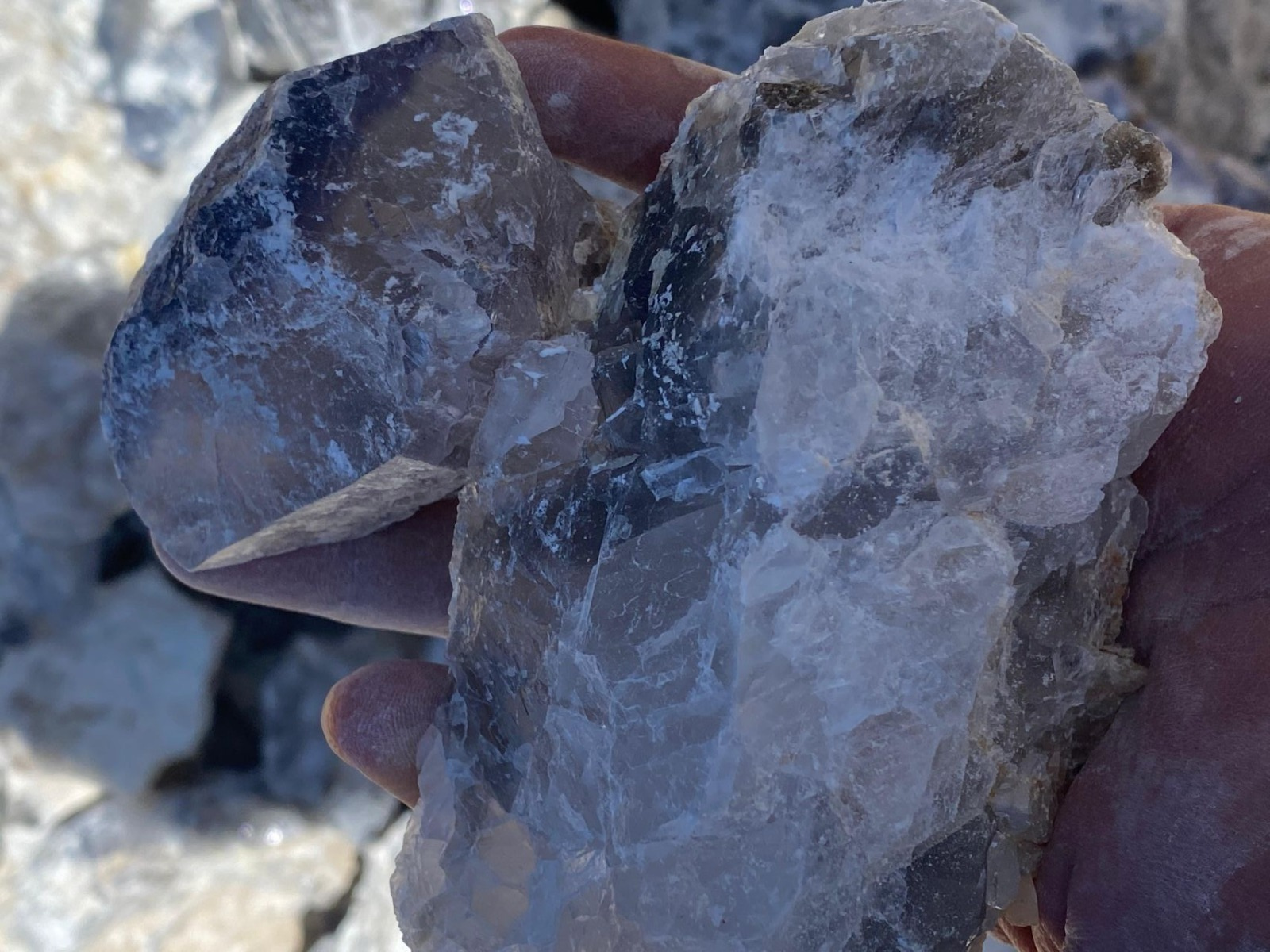
Fluorspar (CaF2)
Fluorspar (CaF2)
Avalibale in lump, chip and powder upto 90% pure
![]()
Calcium fluoride is a mineral composed of calcium fluoride (CaF2), the principal fluorine-bearing mineral. It occurs as cubic, isometric crystals and cleavable masses. When pure, it is colorless and transparent, or translucent with a glassy luster. Impurities cause color in the stone, and several varieties exhibit fluorescence. Usually found either in pure veins or associated with lead, silver, or zinc ores, it is common in limestone and dolomites.
Fluorite comes in a wide range of colors and has subsequently been dubbed “the most colorful mineral in the world”. The most common colors are purple, blue, green, yellow, or colorless. Less common are pink, red, white, brown, black, and nearly every shade in between. Color zoning or banding is commonly present. The color of the fluorite is determined by factors including impurities, exposure to radiation, and the size of the color centers.

![]()
Chemical Name:
Fluorspar
Chemical Formula:
CaF2
Chemical Properties
- Crude ore- 25 to 30%
- Metallurgical grade- 75 to 82%
- Ceramic grade- 94 to 96%
- Acid grade- 97%
- Crystalline grade- 99%
Applications
![]()
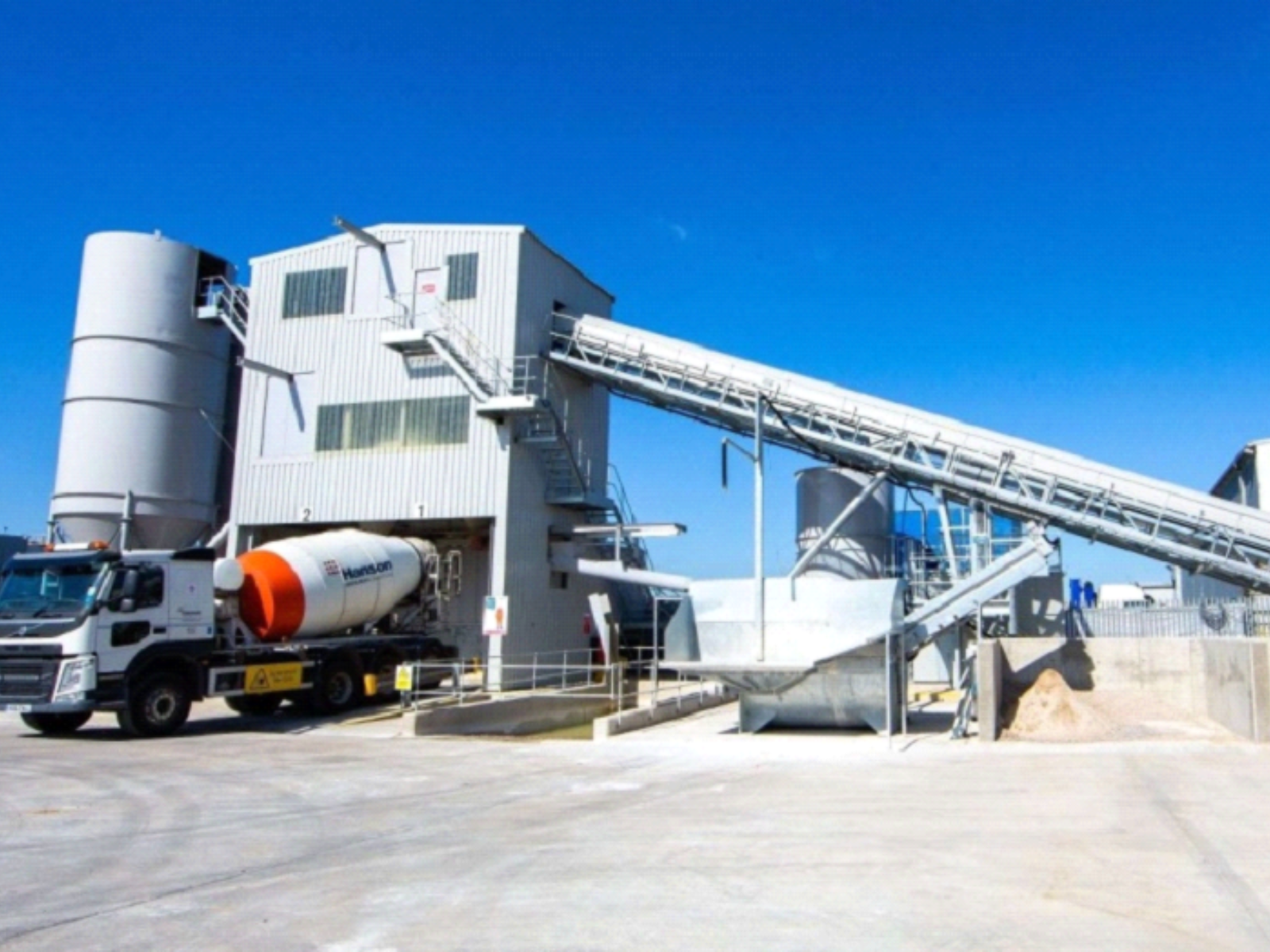

White Cement Production
Fluorspar is an essential additive in the production of white cement, where it serves as a fluxing agent. By lowering the clinkering temperature, fluorspar reduces energy consumption and enhances the whiteness of the cement. This results in a purer white product by preventing the formation of color impurities during the manufacturing process. Additionally, fluorspar improves the overall efficiency of cement production, making it a valuable component in the industry.
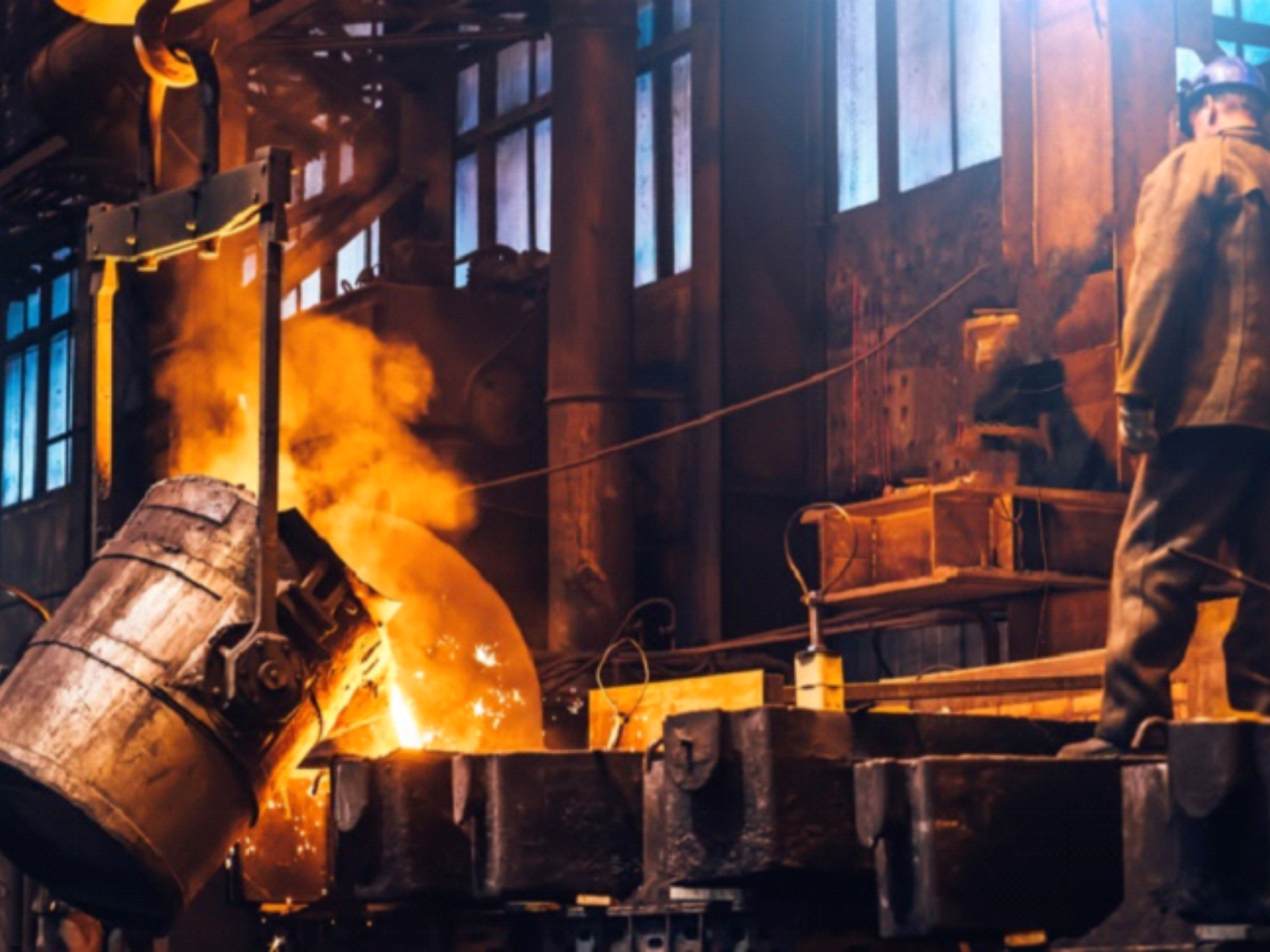

Steel Making
In the steel industry, fluorspar is widely used as a flux to aid in the removal of impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus from molten iron. It reduces the melting point of the raw materials, allowing for a smoother and more efficient refining process. By promoting the formation of slag, fluorspar ensures the separation of impurities from the molten steel, leading to a higher quality final product. Its use in steelmaking contributes to producing cleaner, stronger, and more durable steel.
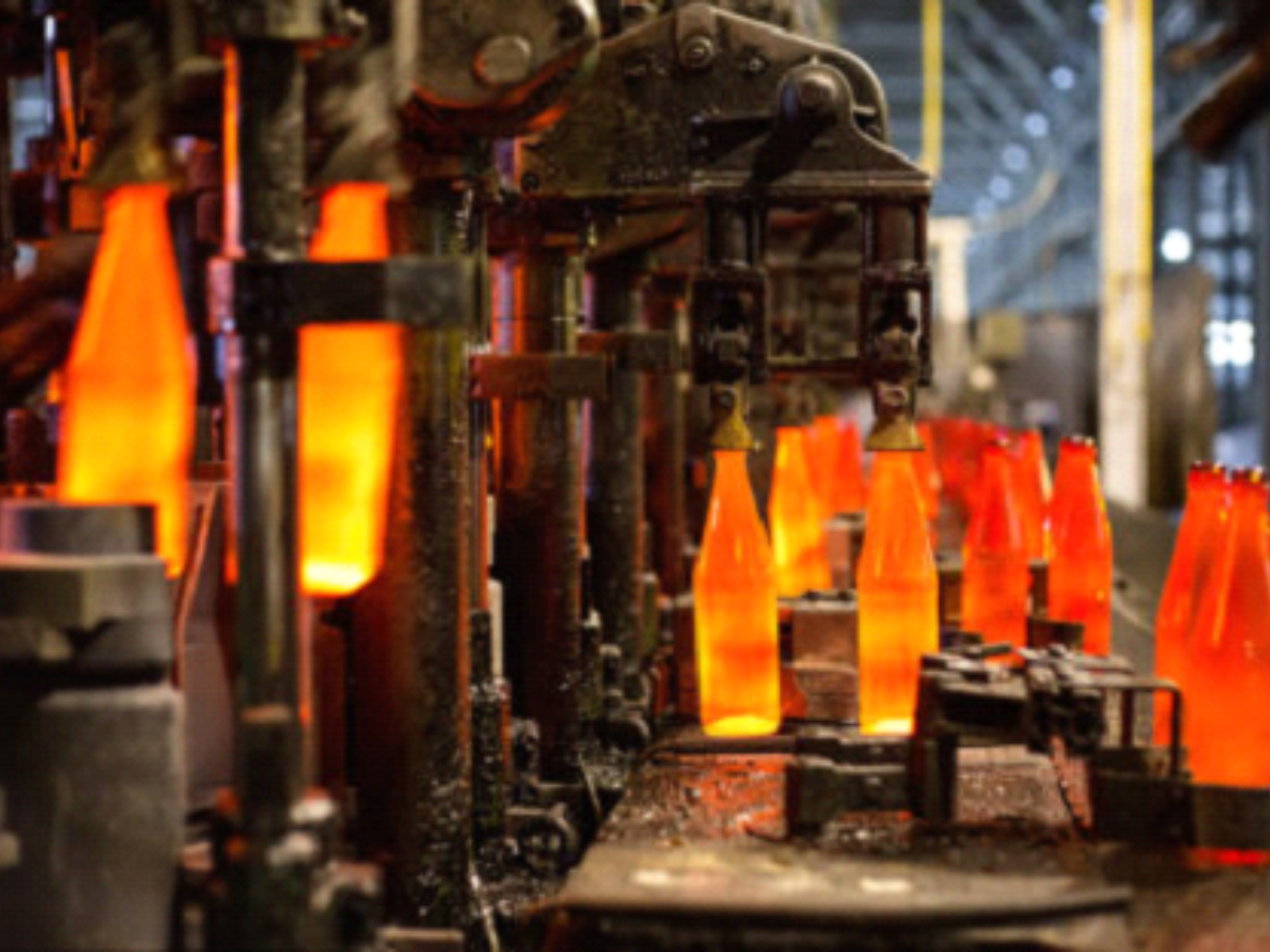

Glass Production
In the glass manufacturing industry, fluorspar is used as a flux to lower the melting temperature of the raw materials, which helps in reducing energy consumption during the production process. It also improves the workability of the molten glass, making it easier to shape and mold into various forms. Additionally, fluorspar enhances the optical properties of the glass, such as clarity and brightness, making it ideal for producing high-quality glass products, including optical lenses, containers, and decorative items.
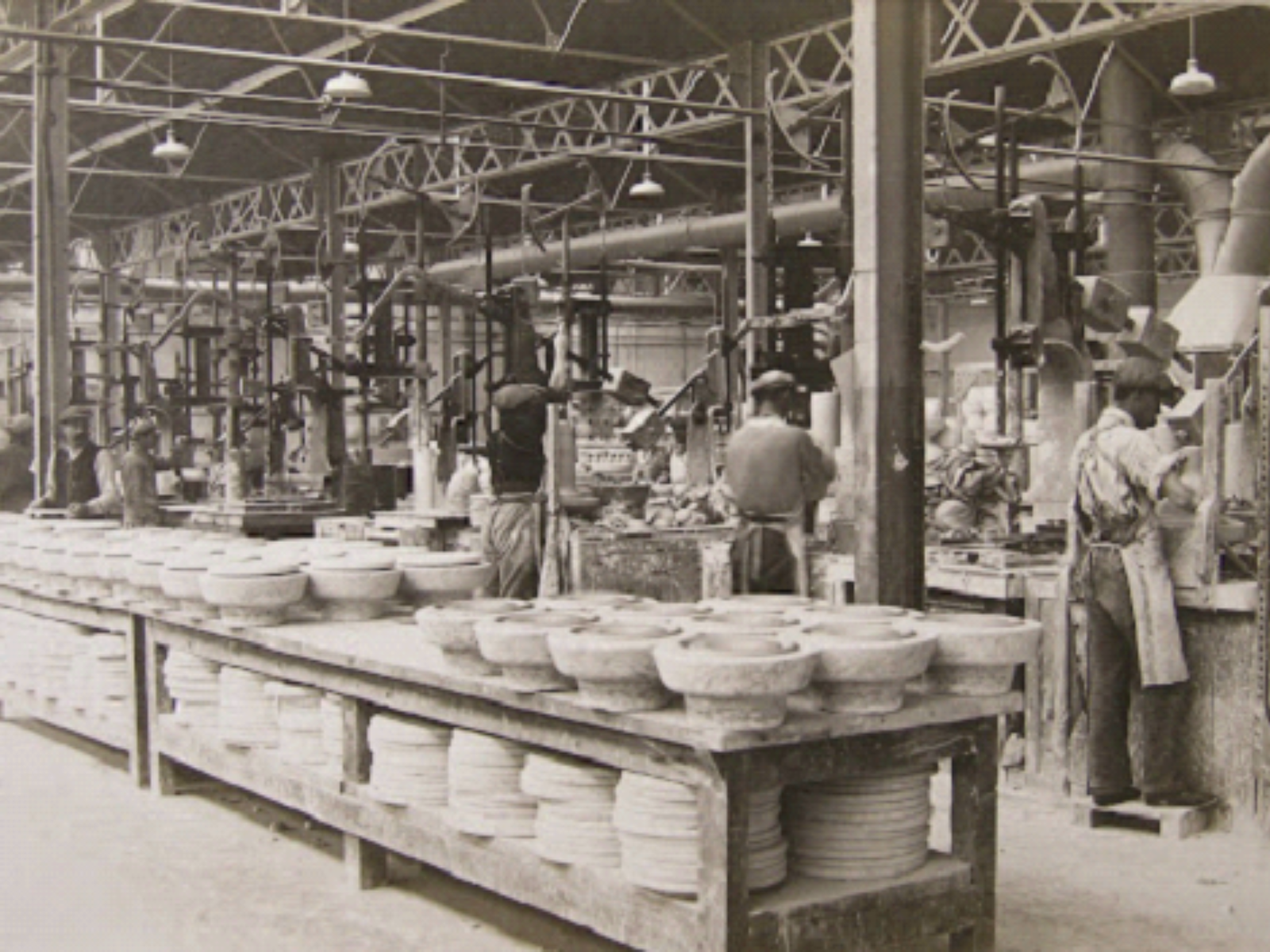

Ceramics Production
In ceramics production, fluorspar plays a crucial role as a fluxing agent, helping to lower the firing temperature of ceramic materials. This reduction in temperature leads to energy savings and improves the efficiency of the kiln operation. Fluorspar also contributes to the formation of a smooth, glassy surface on ceramic items, enhancing their aesthetic appeal and durability. Its use in ceramics is essential for producing fine, high-quality products, ranging from tableware and tiles to specialized industrial ceramics.
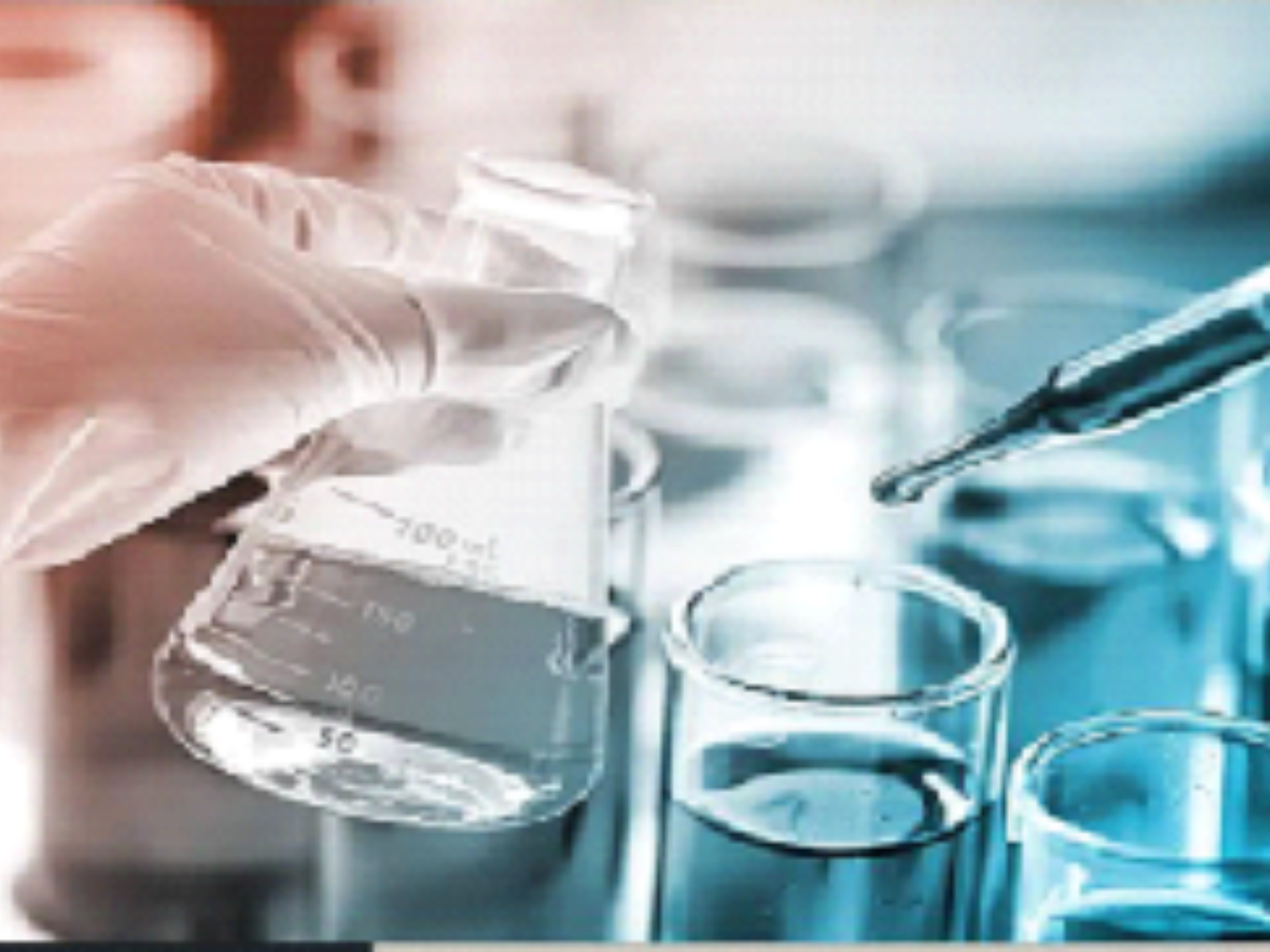

Fluorochemical Production
Fluorspar is the primary source of hydrofluoric acid (HF), which is a crucial precursor in the production of a wide range of fluorochemicals. These chemicals are used in various industries, including the manufacture of refrigerants, pharmaceuticals, and specialty polymers like Teflon. The fluorochemicals produced from fluorspar are integral to many high-tech applications, from air conditioning systems to medical treatments, showcasing the material’s versatility and importance.
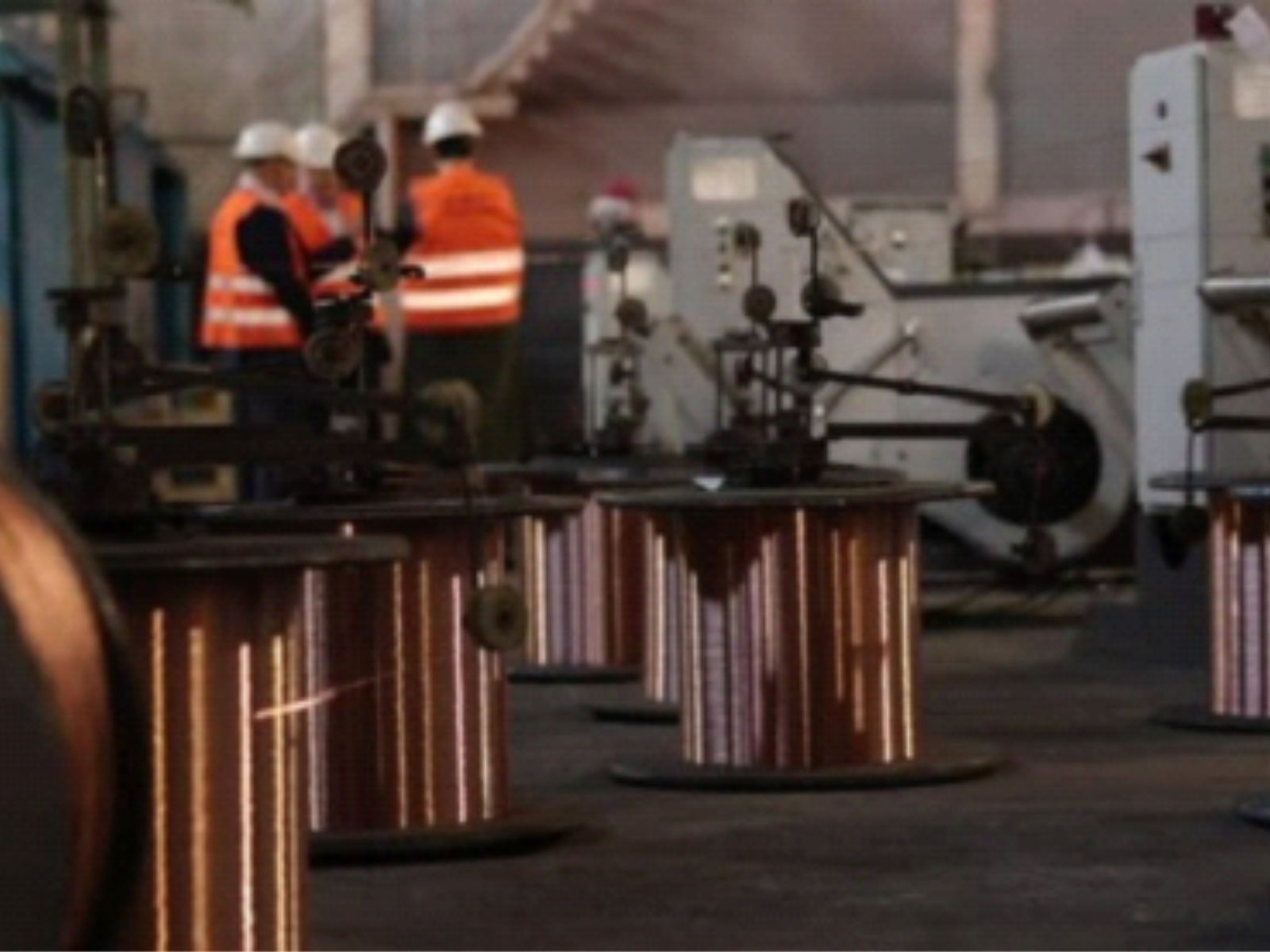

Welding Wire Production
Fluorspar is a key ingredient in the production of welding electrodes and fluxes, which are essential in welding operations. It stabilizes the welding arc and improves the flow of the molten metal, leading to cleaner and more consistent welds. The use of fluorspar in welding materials enhances the quality and durability of the welds, making it a critical component in construction, automotive, and shipbuilding industries.
| Component | Chemical Formula | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Fluoride | CaF2 | 90% max - 60% min |
| Calcium Carbonate | CaCO3 | 15% max - 4.5% min |
| Silica | SiO2 | 20% max - 3.5% min |
| Sulphur | S | 0.05% (constant) |
| Phosphorus | P | 0.05% max - 0.005% min |
| Alumina | Al2O3 | 3% max - 0.5% min |
| Iron | Fe2O3 | 3% max - 1.5% min |
| Moisture Content | - | 1% (constant) |
| Size | Chips | 0-10mm |
| Lumps | 10-70mm |








